About Dengue
Dengue is an arboviral disease caused by infection with any one of four related dengue viral serotypes. It is currently the most important mosquito‐borne viral pathogen affecting humans, and the disease is emerging as a major threat to global health. Best estimates indicate that some 3 billion people live in parts of the world where they are at risk of infection and that around 40 million symptomatic episodes and approximately 20,000 deaths occur each year. It is now reported from over 100 countries around the world, affecting primarily Southeast Asia, Latin America and the Caribbean, with Southeast Asia accounting for approximately 70% of the global dengue morbidity and mortality. In Figure 1.2 the dramatic increase in case numbers reported to WHO over the last 50 years is depicted ‐ however, the true disease incidence is likely to be several‐fold higher since many clinically apparent cases in the community remain undetected by the hospital‐based surveillance systems conventionally relied upon for disease reporting.
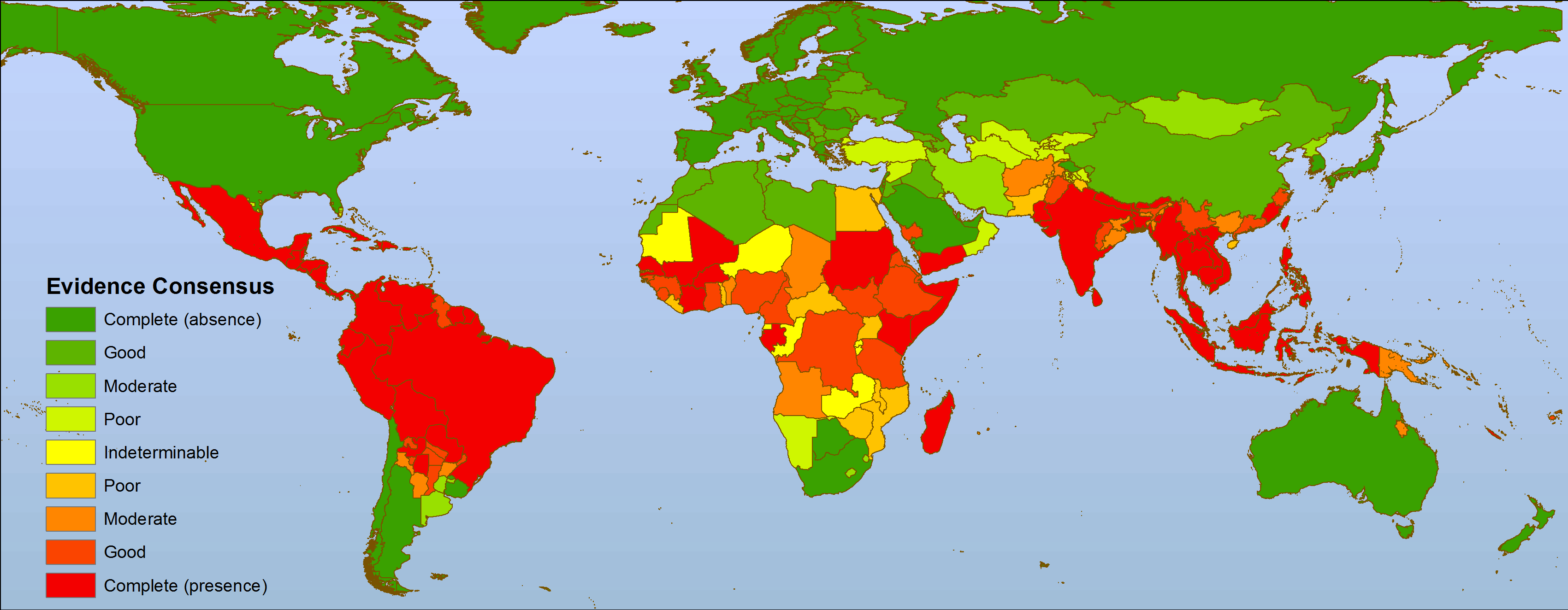 Global map showing the evidence consensus on dengue virus presence and absence (Brady et al., PLoS NTDs 2012)
Global map showing the evidence consensus on dengue virus presence and absence (Brady et al., PLoS NTDs 2012)
